What you’ll learn:
- How to run Cypress tests with webapp.io as part of a CI/CD pipeline
- How to make the filebrowser experience better for your developers
- How to parallelize Cypress test runs within webapp.io
Video Tutorial:
Overview
- Webapp.io + Cypress
- Running Cypress Tests in webapp.io
- Sample App Overview
- Understanding Layerfiles
- Viewing Cypress Results
- Running Tests in Parellel
1. Webapp.io + Cypress:
Cypress is a fast, easy, and reliable end-to-end testing solution for anything that runs in a browser, and webapp.io enables you to review changes to your project within minutes instead of hours. On every commit, webapp.io gives you a customizable full-stack preview environment for your webapp. Leveraging the two together, we can get full-stack review environments that can run our Cypress tests.2. Running Cypress Tests in webapp.io
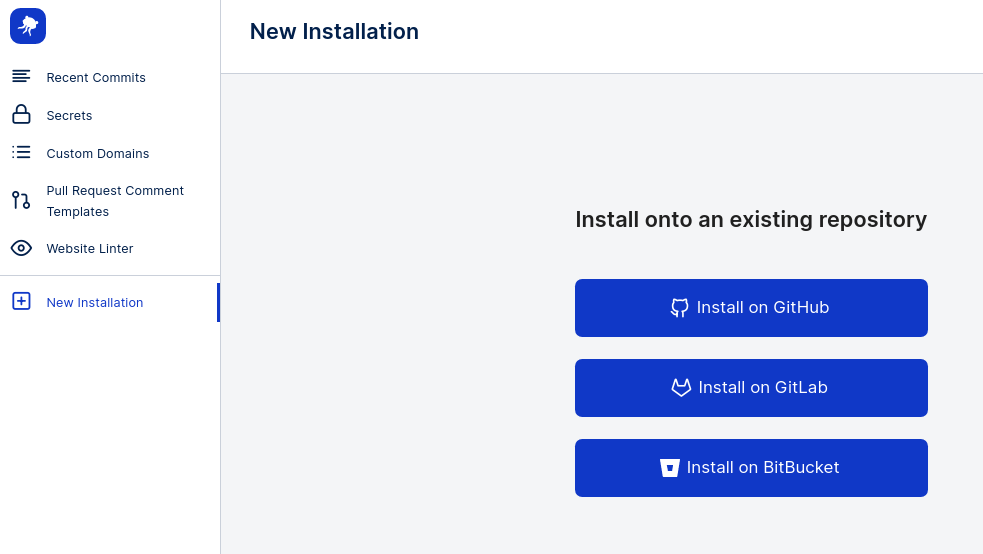
Running Cypress tests in webapp.io is simple with Layerfiles. To run our Cypress tests on a preview environment, we simply need to install webapp.io onto our repository, and push a commit with our Layerfile. First off, head over to webapp.io to sign-up/sign-in.
3. Sample App Overview:
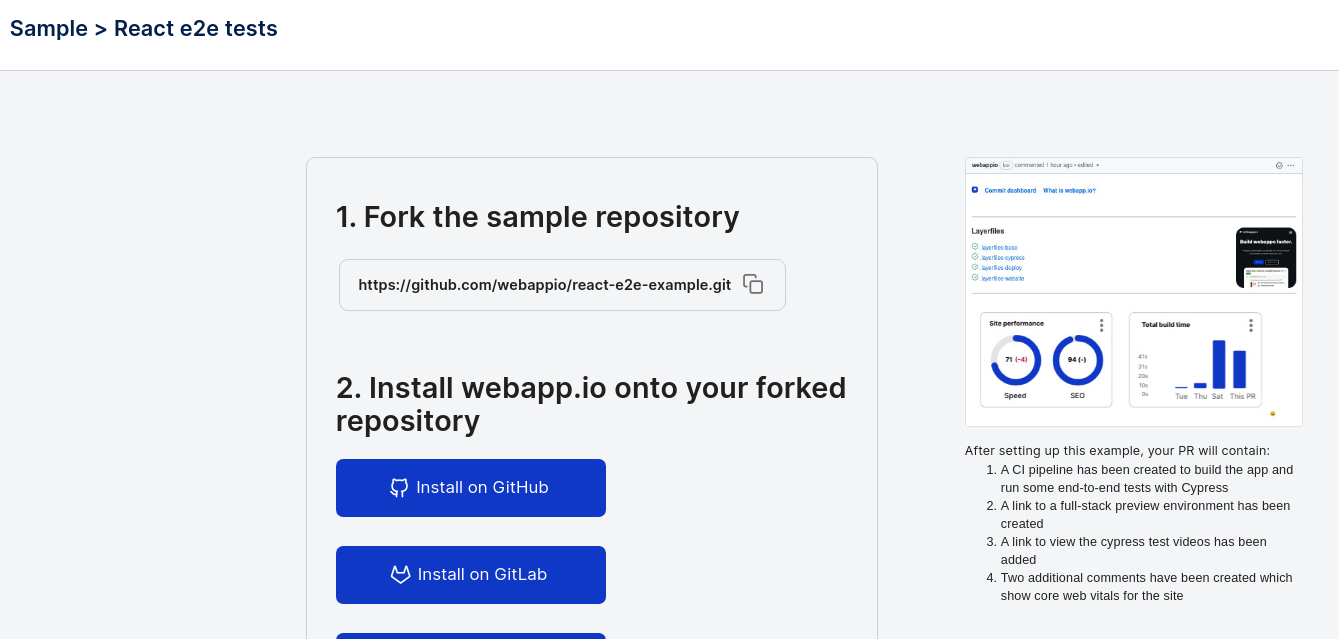
In this tutorial, we’ll go over a sample React app with a Cypress test. The sample React application can be found in the following repository React E2E Example. To run the application, fork the repository, clone the repository to your local computer, and run the commandnpm install in the root folder to install the project dependencies.
Once installed, we can run npm start to start the React project.
To view the file defining our Cypress test, we can navigate to react-e2e-example/tests/test_navigation.spec.js.
The Cypress test in this file checks the links in the React application to ensure
that they all work.
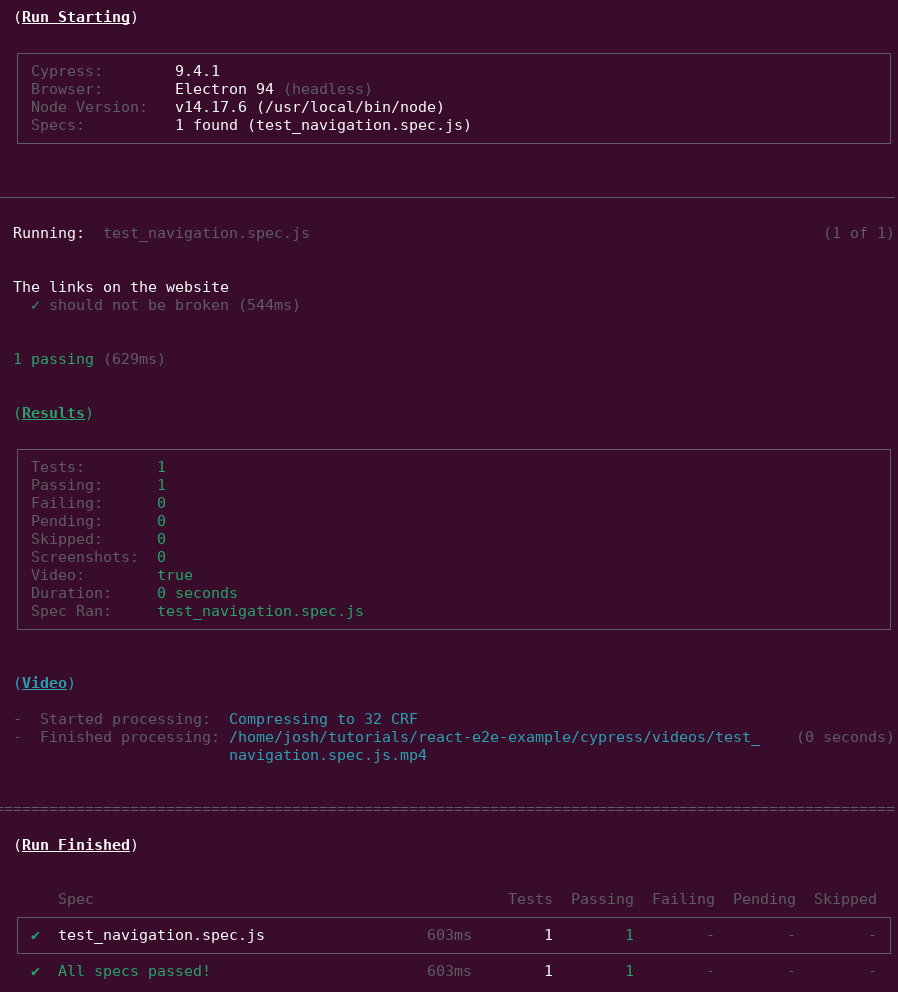
Before running the tests in our preview environment for webapp.io, let’s run it locally
in another terminal with the following command:
npx cypress run
We can see the Cypress tests have passed in the terminal.
4. Understanding Layerfiles
In our sample React application we have a file calledLayerfile. Layerfiles
are a set of instructions that tell webapp.io how to build and run your
application as a preview environment. Let’s break down what the existing
Layerfile does.
Layerfile
FROM vm/ubuntu:18.04
This tells webapp.io what base to run tests from.
Layerfile
RUN command view the
RUN Documentation.
Layerfile
MEMORY instruction allows you to reserve memory before you need it. In
particular, languages like nodejs might require memory to be available before
they are used, so we allocate more memory here.
Layerfile
COPY instruction copies all the files from your repository into the
Virtual Machine from webapp.io. After copied, we create a cypress directory to
store our results, install the dependencies with npm install and start our
React app with npm start. Please note that we use RUN BACKGROUND here so
that webapp.io can proceed to the next step instead of hanging on the React
start process.
Layerfile
npx cypress run to run our cypress tests.
Layerfile
5. Viewing Cypress Results
Now that we’ve understood the Layerfile, simply push a commit from your local repository. After pushing your commit, head over to the webapp.io dashboard to the “Recent Commits” tab where you’ll see a new run starting.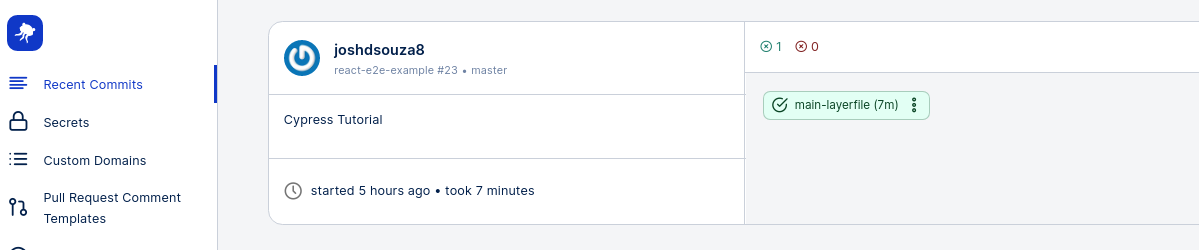
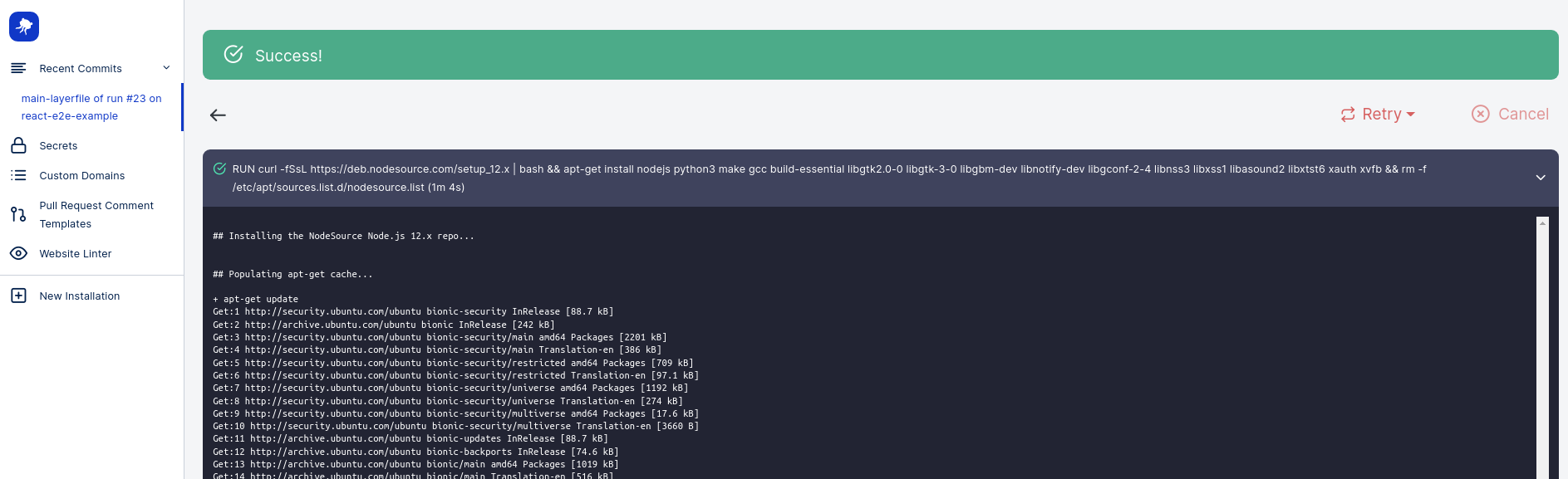
Layerfile
Layerfile
Layerfile
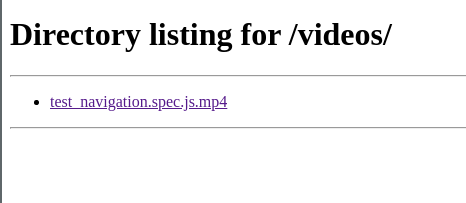
/cypress directory, run filebrowser on port
9000, and expose the website at port 9000.
After committing this Layerfile, we’ll get the following developer experience in
the preview environment:
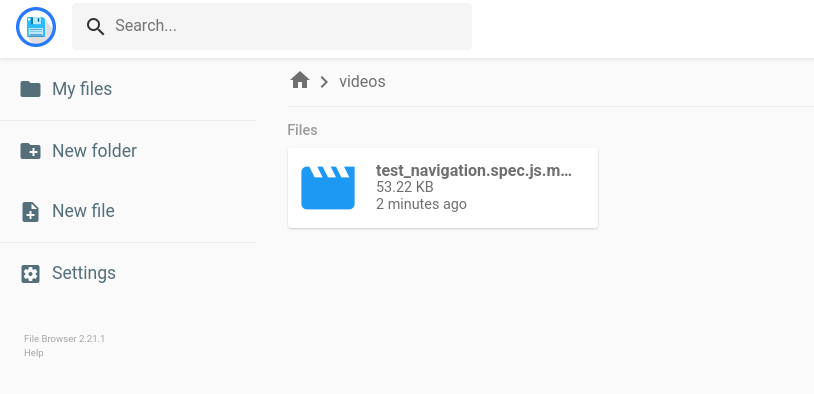
6. Running Tests in Parellel
If your project has a large number of tests, it can take a long time for tests to complete running in series on one machine. Running tests in parallel across many virtual machines can save your team time and money when running tests. This is where the webapp.ioSPLIT instruction comes in. The SPLIT
instruction causes the runner to duplicate its entire state a number of times at
a specific point.
In order to run our tests in parallel and view the associated Cypress test
results, we need to set up an account with Cypress and obtain a Cypress record
key for our project. You can set up an account and project to obtain a key by
going through the following
documentation.
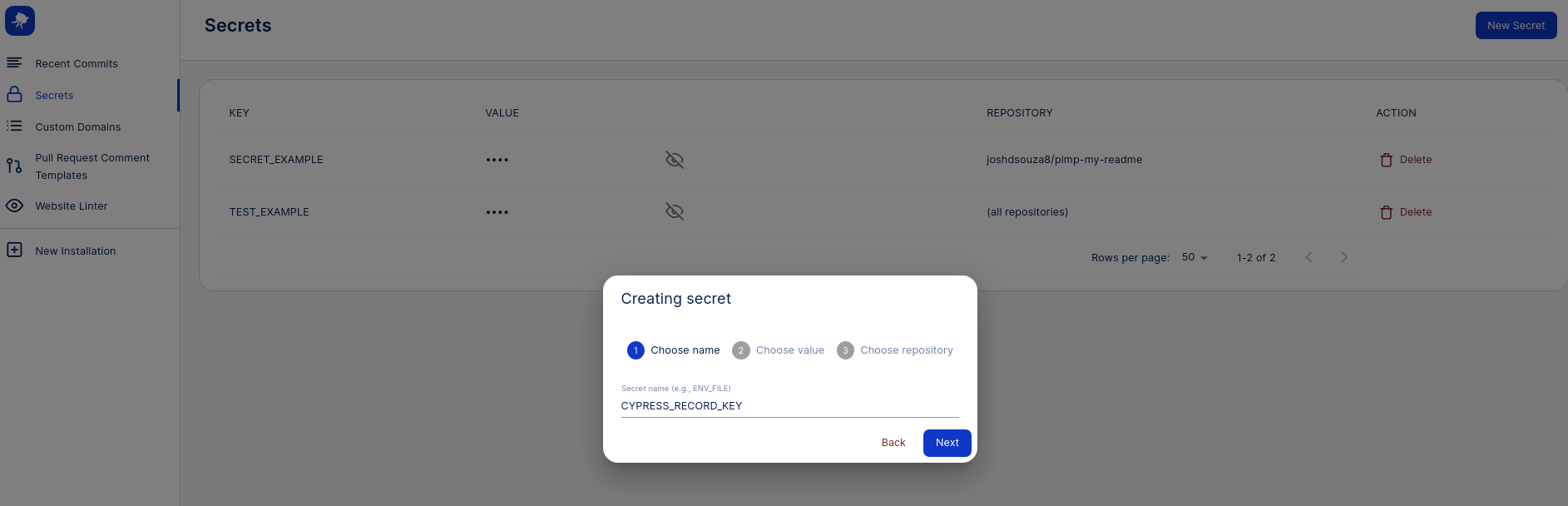
After receiving your project key, add the key to your webapp.io secrets by
navigating to the “Secrets” tab in the dashboard with the following name,
CYPRESS_RECORD_KEY.
test_correct_title.spec.js in the
tests folder with the following content:
Layerfile